Arrhythmia refers to a condition that affects the rhythm of the heart or heartbeat rate, causing it to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly. It can develop silently or with noticeable symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or chest discomfort. Some arrhythmias are harmless, while others may be serious or life-threatening if not treated on time. Recognizing arrhythmia early and seeking the right medical care can play a vital role in controlling the condition and reducing the chances of severe heart-related problems.
At Park Group of Hospitals, we are committed to delivering advanced cardiac care with a patient-first approach. Our state-of-the-art heart care centers offer comprehensive diagnosis, management, and treatment for arrhythmias, including complex cases such as atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, and bradycardia. With expert cardiologists and electrophysiologists, we ensure every patient receives personalized care tailored to their heart health needs.
We offer specialized cardiac treatment for arrhythmia at our leading centers located in Delhi, Gurugram (Sec-47, Palam Vihar, Sec-37 D), Faridabad, Sonipat, Panipat, Karnal, Ambala, Patiala, Mohali, Bathinda, Behror, and Jaipur.
If you or a loved one is experiencing irregular heartbeats or any heart-related symptoms, visit your nearest Park Hospital for expert consultation. For any cardiac emergency, our 24x7 helpline +91 99166 99166 is always available to assist you promptly.
What is Arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia refers to an abnormal rhythm of the heart that occurs when the electrical signals controlling your heartbeat are disrupted. This condition may cause the heart to beat too quickly (tachycardia), too slowly (bradycardia), or in an irregular pattern. While occasional irregular heartbeats are common and often harmless, persistent or severe arrhythmias may signal underlying heart disease and can increase the risk of serious complications, including stroke, heart failure, or sudden cardiac arrest.
In a healthy heart, the electrical impulses follow a specific pathway through the heart’s chambers, ensuring a steady and coordinated beat. In people with arrhythmia, this natural rhythm is affected, leading to noticeable symptoms or sometimes remaining entirely silent. Recognizing and understanding the types of arrhythmias is the first step toward proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Types of Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias can vary greatly in their causes, symptoms, and severity. Understanding the common types of arrhythmias can help in identifying the condition early and deciding the right course of treatment. Below are the major types:
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial fibrillation is a condition that affects the rhythm of the heart. It happens when the upper sections of the heart, known as the atria, begin to beat in an uneven and uncoordinated way compared to the lower sections, called the ventricles. This can lead to poor blood flow and increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart failure.
Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is similar to atrial fibrillation but tends to produce a more regular rhythm. It is caused by abnormal electrical circuits in the atria and can sometimes convert into atrial fibrillation if not treated.
Supraventricular Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia which originates above the heart's ventricles is known as Supraventricular Arrhythmia. It includes conditions like paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) and Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome, where the heart suddenly beats very fast.
Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a condition where the heart beats too slowly, typically fewer than 60 beats per minute. It can be normal in healthy individuals, such as athletes, but in others, it may indicate a problem with the heart’s electrical system and may require a pacemaker.
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is a condition where the heart beats faster than normal, usually over 100 beats per minute at rest. It can cause noticeable symptoms such as a rapid or irregular heartbeat, feeling lightheaded, or in some cases, sudden loss of consciousness.
Ventricular Arrhythmias
These are more serious arrhythmias that originate in ventricles. They include ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, which can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Each of these arrhythmias presents differently and may require distinct diagnostic tests and treatment approaches. Early diagnosis and proper type of classification play a critical role in effective arrhythmia management.
Causes of Arrhythmia
The underlying causes of arrhythmia can range from structural heart problems to lifestyle-related factors. Sometimes, arrhythmias may develop without a clear reason, but often, they are linked to conditions or habits that affect the heart’s electrical system.
Heart-related conditions
Diseases that affect the structure or function of the heart are among the most common causes. These include:
Coronary artery disease
Heart valve disorders
Heart failure
Cardiomyopathy
Previous heart surgery or heart attack
High blood pressure and diabetes
Chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes can damage the heart and its electrical pathways, increasing the risk of arrhythmia.
Electrolyte imbalances
Essential minerals such as potassium, magnesium, sodium, and calcium help regulate heartbeat. When the levels of essential electrolytes in the body become disturbed, it can lead to unusual or irregular heart rhythms.
Excessive alcohol or caffeine
Heavy alcohol use, energy drinks, or high caffeine intake can overstimulate the heart and provoke episodes of atrial fibrillation or tachycardia.
Smoking and recreational drug use
Nicotine and drugs like cocaine or amphetamines can have toxic effects on the heart and its rhythm.
Stress and anxiety
Intense stress or emotion can release adrenaline, which may disturb the heart's rhythm.
Medications
Some over-the-counter cold and cough medications, certain antidepressants, or prescription drugs for other conditions can interfere with normal heart rhythm.
Thyroid disorders
When the thyroid gland produces either too much or too little hormone, it disrupts the body's metabolic balance, which can lead to irregular heart rhythms.
Recognizing the exact cause is essential for effective arrhythmia treatment, as the root condition must be managed alongside the irregular heartbeat itself.
Symptoms of Heart Arrhythmia
Depending on the type and severity of the condition, heart arrhythmia symptoms can vary person to person. While some people may not notice any symptoms, others may experience noticeable and even distressing signs. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely medical evaluation and treatment.
Palpitations
A feeling that your heart is racing, fluttering, skipping beats, or pounding in your chest. This is among the most frequent signs seen in people with arrhythmia.
Dizziness or light-headedness
Irregular or slow heart rhythms can reduce blood flow to the brain, leading to episodes of dizziness or a light-headed sensation.
Shortness of breath
An abnormally fast or slow heartbeat can affect how efficiently your heart pumps blood, making it difficult to breathe during everyday activities or even at rest.
Chest discomfort or pain
Some types of arrhythmias, especially those caused by coronary artery disease, may be associated with chest pain or tightness. This symptom should never be ignored.
Fatigue or weakness
When your heart is not pumping effectively, it may result in constant tiredness, even after minimal exertion.
Fainting or near-fainting episodes (syncope)
You may faint if your blood pressure or heart rate drops suddenly. This can be dangerous, especially if it occurs while driving or operating machinery.
Anxiety or a sense of unease
People with arrhythmias may feel anxious or panicked without an obvious cause. This is your body’s response to an irregular heart rhythm.
Some arrhythmias are harmless and may not require treatment. However, persistent or severe symptoms may point to an underlying heart condition that demands urgent attention. It is always safer to get evaluated by a heart specialist if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above.
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing arrhythmia involves a detailed review of your symptoms, medical history, and a range of specialized heart tests. Since arrhythmias can be occasional or silent, capturing them requires accurate and sometimes continuous monitoring.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An electrocardiogram is the most common and effective test for detecting arrhythmias. It captures the electrical signals generated by your heart and helps identify any irregular rhythms, unusually slow or fast heart rates, or evidence of a past heart attack.
Holter Monitor
This is a portable ECG device worn for 24 to 48 hours that records your heart’s rhythm over a longer period. It is especially useful for detecting intermittent arrhythmias that may not appear during a standard ECG.
Event Monitor
Similar to a Holter monitor, an event recorder is worn for weeks and activated only when symptoms occur. It helps detect arrhythmias that are infrequent but still significant.
Echocardiogram
An ultrasound of the heart, the echocardiogram provides images of the heart’s structure and function. It can identify structural heart issues that may cause or worsen arrhythmias.
Stress Test
This test measures your heart’s electrical activity during physical exertion. It helps detect arrhythmias triggered by exercise or physical stress and assesses your overall heart health.
Electrophysiology Study (EPS)
An EPS is an advanced test in which thin wires are inserted into the heart through blood vessels to study the electrical signals. It helps pinpoint the source of an arrhythmia and is often used before procedures like catheter ablation.
Blood Tests
These are done to check for underlying conditions like thyroid problems, electrolyte imbalances, or infections that may trigger arrhythmias.
Correct diagnosis is important for choosing effective arrhythmia treatment. A combination of tests may be required based on the symptoms, severity, and type of arrhythmia suspected.
Treatment Options for Arrhythmia
Heart arrhythmia treatment depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause of the condition. While some arrhythmias may not need any intervention, others require medications, procedures, or devices to correct the heart’s rhythm and prevent complications.
Medications
There are different kinds of medications that doctors to control your heart rate or rhythm:
Antiarrhythmic medications: Restore and stabilize normal heart rhythm.
Beta-blockers: Lower heart rate and control blood pressure.
Calcium channel blockers: Control the rate of certain arrhythmias.
Anticoagulants (blood thinners): Reduce the risk of stroke, especially in conditions like atrial fibrillation.
Cardioversion
This method restores normal heart rhythm using electric pulses or specific medications. Electrical cardioversion is often used for persistent atrial fibrillation.
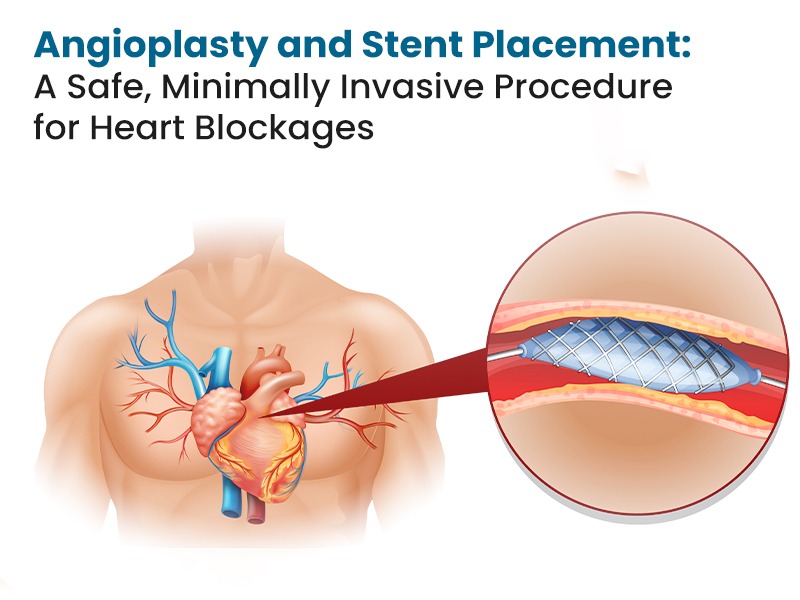
Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure where thin wires are guided through the blood vessels into the heart to destroy the areas causing abnormal rhythms. It is commonly used for supraventricular arrhythmias, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia.
Pacemaker
A pacemaker is a small device placed under the skin near the collarbone. It helps manage slow heart rhythms by delivering gentle electrical pulses that maintain a steady and regular heartbeat.
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD)
An ICD is like a pacemaker but treats dangerous ventricular arrhythmias by delivering shocks to restore normal rhythm. It delivers a shock when it senses a life-threatening rhythm, restoring a normal heartbeat.
Surgery
In rare cases, open-heart surgery may be needed to correct structural issues that are causing arrhythmias, especially when other treatments have not worked.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatments, changes in lifestyle can play a crucial role in managing arrhythmia. These include:
Limiting alcohol and caffeine
Quitting smoking
Managing stress
Controlling blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol
Regular exercise under medical supervision
Effective treatment requires an individualized approach. Consulting a qualified cardiologist or electrophysiologist ensures that you receive the most suitable therapy for your condition.
Arrhythmia Management and Lifestyle Changes
Effective arrhythmia management involves more than just medical procedures or medications. Long-term control and prevention depend heavily on making healthy lifestyle choices, managing risk factors, and staying consistent with follow-up care.
Maintain a Heart-Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can improve overall heart function. Reducing sodium, saturated fats, and processed foods helps control blood pressure and supports stable heart rhythms.
Avoid Stimulants and Triggers
Limit or eliminate substances known to provoke arrhythmias:
Caffeine
Alcohol
Nicotine
Over-the-counter cold medications
Recreational drugs
Always check with your doctor before taking any supplements or medications that may affect heart rhythm.
Exercise Regularly
Engage in moderate physical activity like walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 30 minutes on most days. However, intense workouts should be avoided unless cleared by your doctor, especially in cases of ventricular arrhythmia.
Manage Stress and Anxiety
High stress levels can worsen or trigger arrhythmias. Practice stress-reduction techniques like:
Deep breathing
Yoga or meditation
Mindfulness therapy
Spending time in nature or with loved ones
Control Underlying Health Conditions
Keep conditions like hypertension, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and high cholesterol in check. These issues significantly impact heart rhythm and long-term outcomes.
Follow Up with Your Cardiologist
Regular checkups are essential, even if your symptoms have improved. Your doctor may adjust medications, order periodic tests, or recommend additional procedures based on your heart’s performance.
Medication Adherence
Take your prescribed medications exactly as directed. Missing doses or stopping treatment on your own can lead to dangerous recurrences or complications.
By actively participating in your care and making heart-healthy lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of arrhythmia episodes and enjoy a better quality of life.
When to See a Doctor or Cardiologist
While not all irregular heartbeats are dangerous, some may signal serious underlying heart problems. Knowing when to seek medical help for arrhythmia is crucial for early intervention and preventing complications.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
Fainting or near-fainting episodes
Severe chest pain or pressure
Shortness of breath at rest
Sudden dizziness or confusion
A racing or fluttering heartbeat that does not stop
These symptoms may indicate life-threatening forms of arrhythmia, such as ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, which require urgent treatment.
Consult our cardiologist if you notice any irregular heart-related symptoms:
Frequent palpitations or skipped heartbeats
Persistent fatigue or weakness
Unexplained light-headedness
Irregular heart rhythms during physical activity
Family history of heart disease or arrhythmia
Early evaluation by a heart specialist can help identify the cause of your symptoms and start you on a suitable treatment plan. If you have already been diagnosed with arrhythmia, regular follow-ups ensure your condition is well-managed and complications are avoided.
For expert guidance, consult with the cardiology team at Park Group of Hospitals, where we offer comprehensive care tailored to your heart’s needs.
Advanced Arrhythmia Care at Park Group of Hospitals
At Park Group of Hospitals, we specialize in diagnosing and treating all types of arrhythmias with cutting-edge technology and expert-led care. Whether you're experiencing occasional palpitations or have been diagnosed with a complex rhythm disorder like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, our team is equipped to provide personalized solutions that prioritize your heart’s long-term health.
Our hospitals are equipped with:
Advanced electrophysiology labs
3D mapping systems for catheter ablation
Cardioversion and pacemaker implantation facilities
State-of-the-art diagnostic and monitoring tools
Cardiac rehabilitation programs
We have a dedicated team of experienced cardiologists, electrophysiologists, cardiac surgeons, and trained nurses working together to ensure seamless, multidisciplinary care. From diagnosis and treatment to lifestyle counselling and follow-up, our focus is on offering holistic care tailored to each patient.
If you or your loved one is facing symptoms of an irregular heartbeat or has been diagnosed with any form of arrhythmia, reach out to your nearest Park Hospital for a detailed evaluation and compassionate care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How dangerous is arrhythmia and what exactly does it mean for your heart?
Arrhythmia is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly, either too fast, or too slow. While some types are harmless and temporary, others can be serious or even life-threatening, especially if they affect blood flow to vital organs. Timely diagnosis and proper management are essential to avoid complications like stroke, heart failure, or cardiac arrest.
What are the early signs of arrhythmia?
Early signs may include palpitations, dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, or a fluttering feeling in the chest. Some people may also feel light-headed or experience brief blackouts. If you are feeling any of these symptoms frequently, consult a cardiologist for evaluation.
Can stress or anxiety cause arrhythmia?
Yes. Emotional stress, panic attacks, or chronic anxiety can lead to irregular heart rhythms, especially in people already at risk. High levels of stress hormones like adrenaline can overstimulate the heart, causing atrial fibrillation or tachycardia.
Is arrhythmia curable?
Some arrhythmias can be cured, especially those triggered by reversible causes like electrolyte imbalances or certain medications. Others may require lifelong management with medications, catheter ablation, or implanted devices like pacemakers or defibrillators. The primary objective is to manage the symptoms effectively while minimizing potential health complications.
Can lifestyle changes prevent arrhythmia?
In many cases, yes. Avoiding alcohol, caffeine, and smoking, managing stress, eating a heart-healthy diet, and exercising regularly can reduce the risk of developing arrhythmia or improve its management.