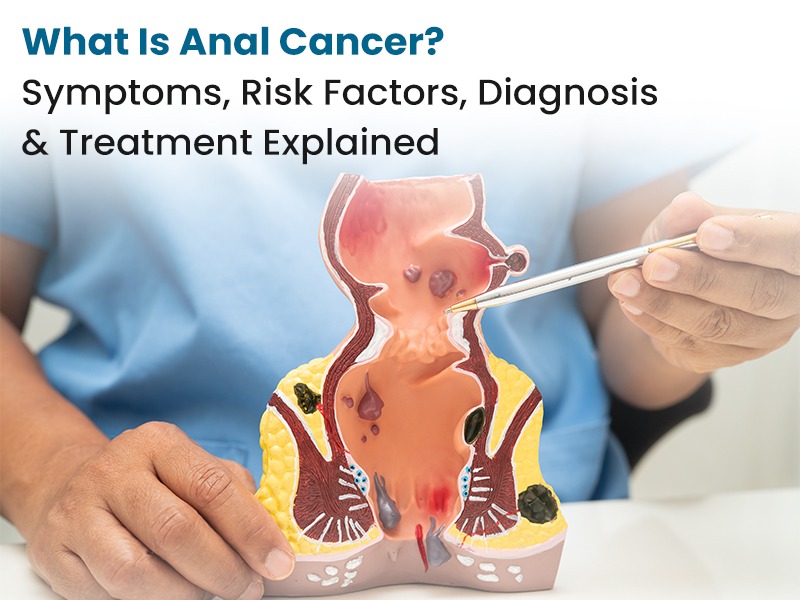
Anal cancer starts in the anus, the opening at the end of the digestive tract. It occurs in nearly 1 per 2200 individuals in India (Indian Journal of Medical Research, 2023). Even though it is a rather uncommon disease, it has become more prevalent in recent years, especially because of the infections caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is considered one of the most common anal cancer causes, and most of the squamous cell carcinomas of the anal region are related to this virus.
Continue reading to know what anal cancer is, its symptoms, causes, types, diagnosis and its treatments.
How Many Types of Anal Cancer Are There?
Forms of abnormal cell growth of the anus include anal intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN) or anal squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL). Anorectal tumours are either benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous) tumours. The various forms of anal carcinoma and their location include:
Adenocarcinoma is found in the mucus-producing glands under the lining of the anus.
Basal cell carcinoma is a skin cancer found in the skin around the anus.
Melanoma, a skin cancer found in the pigment-producing cells of the skin or the lining of the anus. Squamous cell carcinoma at the anal canal outer wall of the anal canal
Cloacogenic carcinoma that occurs between the outer part of the anus and the part of the rectum
Adenocarcinoma that occurs in glands under the anal lining and produces mucus
What Are the Common Anal Cancer Symptoms?
Approximately 2 out of every 10 individuals diagnosed with anal cancer are without symptoms. Certain symptoms of anal cancer are associated with other disorders, like haemorrhoids. But in case you observe any of these symptoms, you should visit your doctor.
Itchy anus symptoms cancer that doesn't go away.
A lump or growth in the anus.
Alterations to bowel movements, including narrowing and increasing or straining passage of stools.
Anal and perianal pain.
Anal secretions, pus and anal mucus.
Blood in the rectum or in the anus.
The groin and anus lymph nodes are swollen.
Staging of Anal Cancer
The stages of anal cancer are categorised into the following:
What are the Causes and Risk Factors for Anal Cancer?
The factors leading to the development of anal cancer are several, such as the human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, smoking, weakening of the immune system, and some lifestyle decisions. Here's what causes anal cancer and increases your risk of developing it:
HPV Infection: HPV infection, specifically, high risk strains, HPV-16 and HPV-18, are linked to most cases of anal cancer, which is about 91%.
Smoking: Smokers are at a much greater risk of developing anal cancer as compared to non-smokers.
Decreased immunity: Individuals who have weakened immunity, like people with HIV or individuals undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are at risk.
Lifestyle Factors: There are some lifestyle factors, including anal sex and multiple sexual partners, which may increase the risk of HPV infection and eventually lead to anal cancer.
Also Read : Most Common Cancer in Women: Types of Female Cancer You Should Know
What are the Treatment Options for Anal Cancer?
The choice of treatment will rely on the stage of the cancer, its location, and the overall condition of the patient. Early diagnosis by cancer specialists often allows for effective organ-sparing therapy.
Chemoradiotherapy
The first-line treatment involves the combination of chemotherapy (5-fluorouracil mitomycin C) and external radiation. This kills cancer cells effectively and usually eliminates the need of a cancer surgery.
Surgery
The surgery is aimed at curing persistent or recurrent cancer following chemoradiotherapy. Local excision can be used to remove small tumours, whereas more developed cases might necessitate abdominoperineal resection (APR), which is becoming less common because of the better treatment options.
Targeted Therapy
Oncologists also employ some medications that attack molecular targets of cancer cells and leave normal tissue untouched. They are also applicable during progression or recurrence.
Immunotherapy
Checkpoint inhibitors, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, may be used in advanced or treatment-resistant cases, especially if the tumour expresses PD-L1 or is associated with HPV.
Prevent Anal Cancer with Prompt Screening and Treatment!
Anal canal cancer is a relatively rare cancer that is closely related to HPV. Getting vaccinated against HPV and talking to your doctor about changes in your anal area can help reduce your risk of developing anal cancer and its complications. If you are at high risk, consider asking your doctor for a screening test.
Park Hospital is considered one of the best cancer hospitals in Delhi. We are committed to providing reliable diagnostic and preventive health solutions for everyone. Contact us for the highest standards of precision and reliability in your anal cancer treatment planning!
Also Read : Simple Diet Swaps for a Cancer-Protective Lifestyle
FAQs
1. What is anal cancer?
Anal cancer is a rare cancer that starts in the cells of the anus (the body's faecal outlet) or anal canal. DNA mutations caused by HPV infection often cause cells (tumours) to grow abnormally.
2. What are common symptoms of anal cancer?
Anal cancer can cause symptoms such as rectal bleeding, bloody stools, and anal pain.
3. Who is at higher risk of anal cancer?
The risk of developing anal cancer depends on many factors, including age and lifestyle. Being infected with HPV is the biggest risk factor for anal cancer.
4. How is anal cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis of anal cancer includes a physical examination and anoscopy, tissue biopsy of the suspicious area, and imaging tests (CT, MRI, PET) to determine the spread, confirmation, and effective staging of the cancer.
5. What treatment options are available?
Treatment options include curative, palliative, and preventive methods. Traditional methods include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, and complementary approaches include acupuncture, yoga, and counselling.